SENSORY INTEGRATION
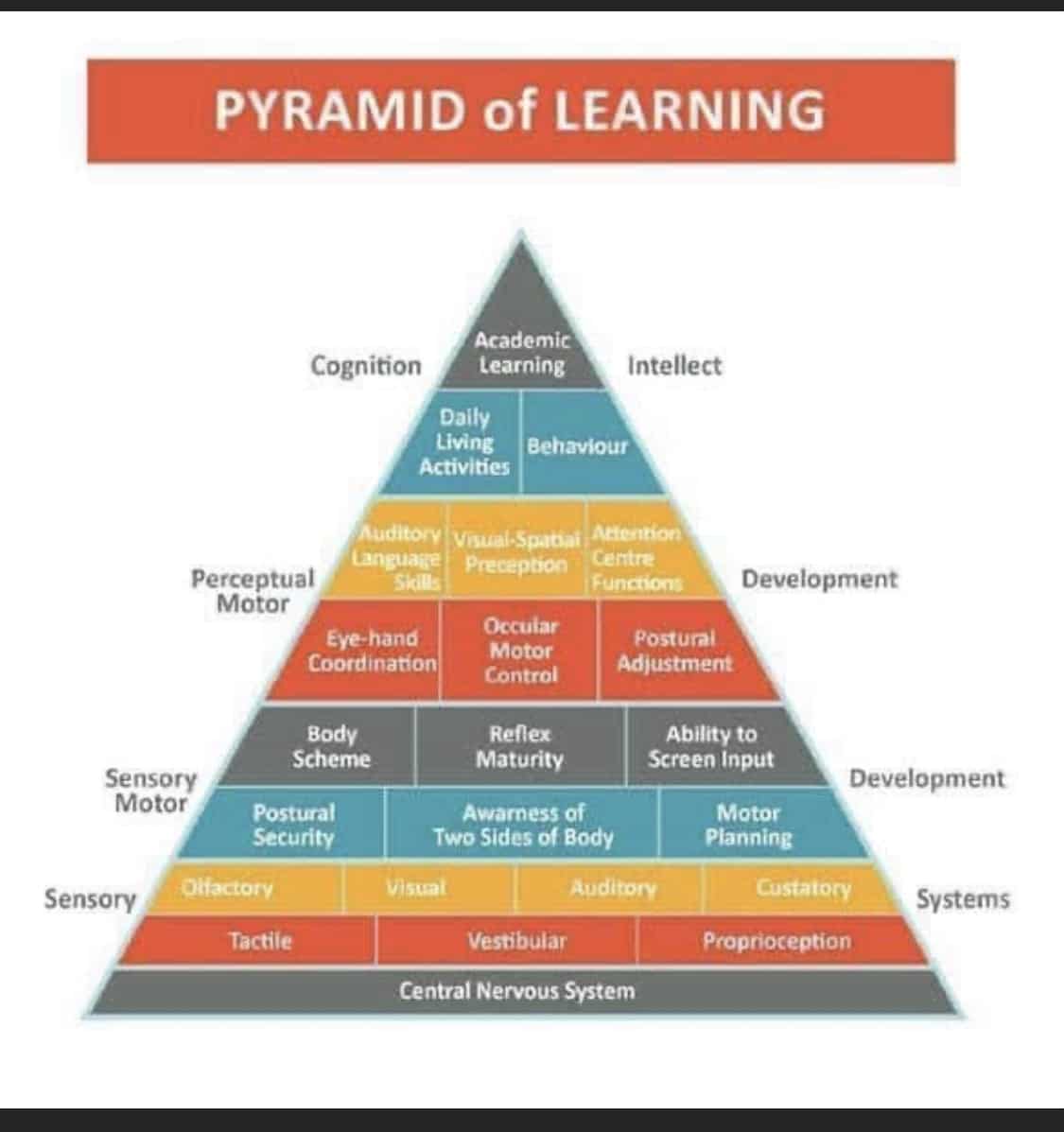
Sensory Processing Disorder (SPD) is defined as a neurological disorder that results from the brain’s inability to integrate certain information received from the bodies 7 sensory systems (tactile, visual, auditory, olfactory, taste, vestibular, proprioceptive). These systems are responsible for detecting and registering sights, sounds, smells, tastes, temperatures, pain, and the positions and movement of the body. From this information, the brain forms a combined picture of its surroundings and reacts to them appropriately. All sensory systems work together to help people learn, to attend, read, write, do math, participate in motor activities, and participate in daily activities. Taking in sensory information in an accurate manner, elicits a functional adaptive motor or behavioral response. The ongoing relationship between behavior and brain functioning as it relates to interpreting sensory information if referred to as sensory integration (SI). This process occurs automatically, unconsciously, and without effort for most people. For others, the process is inefficient or incomplete, and requires extensive effort and attention for sensory integration to occur. SPD can effect level of arousal, attention, emotional behavior, social relationships, as well as motor skill functioning. Hypersensitivity can elicit a “fight” or “flight” response, and hyposensitivity can elicit not enough engagement to be successful developmentally or with various tasks.


The normal process of SI begins before birth and continues throughout life. The majority of SI development occurs before early teenage years. The ability for SI to become refined and effective coincides with the aging process. It determines how motor and speech skills and emotional stability develop. It provides a crucial foundation for complex learning and behavior throughout life.
Occupational Therapists are important in the treatment of SPD. They provide sensory integration therapy to supply vital sensory input and experiences that allow children to practice and develop SI skills. SPD treatment is individualized and designed to meet the needs of the child’s neurological system. The child’s interests are used to motivate them in treatment and to allow them to be actively involved and explore sensations that are beneficial to them. With practice and continued therapy, as well as carry through at home and at school, children become more mature, less anxious within their environments, and more efficient in organizing sensory information for functional behavioral and motor responses.